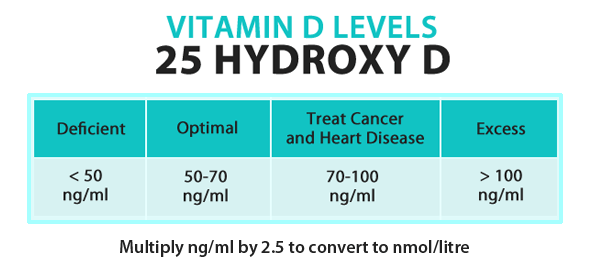
Some 40 leading vitamin D experts from around the world currently agree that there's no specific dosage level at which "magic" happens; rather the most important factor when it comes to vitamin D is your serum level (the level of vitamin D in your blood). So you really should be taking whatever dosage required to obtain a therapeutic level of vitamin D in your blood.

Key Ingredients found in Isotonix® Vitamin D with K2:
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol): 5000 IU
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is found in some foods and endogenously produced when sunlight strikes the skin and activates vitamin D synthesis. Vitamin D promotes the efficient intestinal absorption of calcium, primarily in the duodenum and jejunum by supporting the synthesis of calcium-binding proteins to promote normal calcium absorption and retention. Vitamin D also promotes the normal formation of bone and normal bone growth and bone remodeling by osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Vitamin D deficiency can be caused by factors such as lack of exposure to sunlight, reduced skin synthesis of vitamin D, lower dietary intake, impaired intestinal absorption, and reduced metabolism to active forms of vitamin D by the kidneys, all of which increase with aging. Deficiency has been linked to numerous health concerns, and insufficient levels of this vitamin are associated with weak bones and muscle weakness. In addition to promoting strong bones, vitamin D also has other roles in health, including supporting the body’s normal modulation of neuromuscular function and immune function. Vitamin D has been shown to support immune-modulation, and it is thought that supplementation promotes immune health by promoting the body’s normal regulation of T-cell function. In reference to cellular health, Vitamin D supports the modulation of many genes that are responsible for encoding proteins that regulate normal cell cycle activity. Vitamin D levels have been strongly correlated to healthy cells. Lastly, through its interaction with VDR (vitamin D receptor), vitamin D supports the healthy expression of the gene encoding renin, thus helping to maintain healthy blood pressure.*
Vitamin K2: 45 mcg
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin found meat, eggs, dairy and natto. Although a fat-soluble vitamin, the body stores very little K2, and its stores are rapidly depleted without regular dietary intake. Natural vitamin K2, also known as menaquinone-7 (MK-7), is the most bioavailable form of K2 and has the longest half-life in the blood of any form of vitamin K. The Japanese soy food natto is particularly rich in menaquinone-7 (MK-7). Studies of natto consumption in Japan have linked menaquinone-7 to bone and cardiovascular health. The correlation of vitamin K to cardiovascular and bone health directly focuses on supporting proper calcium utilization, whereby adequate metabolism of calcium supports arterial and bone health. This is often referred to as the calcium paradox. The calcium paradox is explained simply as getting calcium in the right place (i.e., into the bone structures instead of the arterial vessel walls). These events are dependent upon the synthesis of the vitamin K-dependent proteins osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein in a process called carboxylation. The carboxylation of these proteins is a post-translational step; that is, osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein are translated from their respective messenger RNA and then modified by enzymes to the active forms. These carboxylated forms support the healthy binding and releasing of calcium. This reaction is essential for optimal and healthy utilization of calcium. Vitamin K2 promotes the synthesis of proteins involved with calcium utilization, thereby supporting bone retention and arterial health. While vitamin D supports the healthy regulation and synthesis of osteocalcin, the mineral-binding capacity of this protein requires vitamin K-dependent carboxylation and is thought to be related to bone mineralization. Gas6 is a vitamin K-dependent protein found throughout the nervous system, as well in the heart, lungs, stomach, kidneys and cartilage. Although the exact mechanism of its action has not been determined, Gas6 appears to be a cellular growth regulator involved in cellular activities such as cell adhesion, cell proliferation and protection against apoptosis.*
Scientific Studies Which Support Isotonix® Vitamin D with K2:
· Knapen M et al. Vitamin K2 supplementation improves hip bone geometry and bone strength indices in postmenopausal women. Osteoporosis International. 18(7):963-72, 2007.
· Shiraki, M., et al. Vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) effectively prevents fractures and sustains lumbar bone mineral density in osteoporosis. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research. 15:515-522, 2000.
· Hiruma Y et al. Vitamin K(2) and geranylgeraniol, its side chain component, inhibited osteoclast formation in a different manner. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications. 314(1):24-30, 2004.
· Plaza S and Lamson D. Vitamin K2 in bone metabolism and osteoporosis. Alternative Medicine Reviews. 10(1):24-35, 2005. Review.
· Kameda T et al. Vitamin K2 inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption by inducing osteoclast apoptosis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 220(3):515-519, 1996.
· Taira H et al. Menatetrenone (vitamin K2) acts directly on circulating human osteoclast precursors. Calcified Tissue International. 73(1):78-85, 2003.
Hidaka T et al. Treatment for patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis who have been placed on HRT and show a decrease in bone mineral density: effects of concomitant administration of vitamin K(2). Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism. 20(4):235-239, 2002.
· Iwamoto J et al. Effects of vitamin K2 on osteoporosis. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 10(21):2557-2576, 2004.
· Iwamoto J et al. Treatment with vitamin D3 and/or vitamin K2 for postmenopausal osteoporosis. The Keio Journal of Medicine. 2003 Sep;52(3):147-50. Review.
· Neogi, T., et al. Low vitamin K status is associated with osteoarthritis in the hand and knee. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 54(4):1255-1261, 2006.
Price P. Role of vitamin K-dependent proteins in bone metabolism. Annual Review of Nutrition. 8:565-583, 1988.
· Bekner K. The vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Journal of Nutrition. 130(8):1877-1880, 2000.
· Nelsestuen G et al. Vitamin K-dependent proteins. Vitamins and Hormones. 58:355-389, 2000.
· Shearer M. Role of vitamin K and Gla proteins in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and vascular calcification. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 3(6):433-438, 2000.
· Gundberg C et al. Vitamin K status and bone health: an analysis of methods for determination under carboxylated osteocalcin. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 83(9):3258-3266, 1998.
· Weber P. Management of osteoporosis: is there a role for vitamin K? International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research. 67(5):350-6, 1997.
· Garber, A. K., et al. Comparison of phylloquinone bioavailability from food sources or a supplement in human subjects. Journal of Nutrition. 129(6):1201-1203, 1999.
· Binkley N et al. Vitamin K nutrition and osteoporosis. Journal of Nutrition. 125(7):1812-1821, 1995.
· Bischoff-Ferrari Het al. Fracture prevention with vitamin D supplementation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 293(18):2257-2264, 2005.
· Guirguis-Blake J et al. Oral vitamin D3 decreases fracture risk in the elderly. Journal of Family Practice. 52(6):431-435, 2003.
· Schaafsma, A., et al. Vitamin D3 and vitamin K1 supplementation of Dutch postmenopausal women with normal and low bone mineral densities: effects on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and carboxylated osteocalcin. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 54:626-631, 2000.
· Trivedi Det al. Effect of four monthly oral vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) supplementation on fractures and mortality in men and women living in the community: randomised double blind controlled trial. British Medical Journal. 326(7387):469, 2003.
· Van den Berghe G et al. Bone turnover in prolonged critical illness: effect of vitamin D. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 88(10):4623-4632, 2003.
· Chapuy M et al. Vitamin D3 and calcium to prevent hip fractures in the elderly women. New England Journal of Medicine. 327(23):1637-1642, 1992.
· Grant W and Holick M. Benefits and requirements of vitamin D for optimal health. Alternative Medicine Review. 10:94-111, 2005.
· Plaza S and Lamson D. Vitamin K2 in bone metabolism and osteoporosis. Alternative Medicine Reviews. 10(1):24-35, 2005. Review.
· Zitterman A et al. Low vitamin D status: a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of congestive heart failure? Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 41(1):105-112, 2003.
· Schleithoff S et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves cytokine profiles in patients with congestive heart failure: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 83(4):754-759, 2006.
Argiles A et al. Blood pressure is correlated with vitamin D(3) serum levels in dialysis patients. Blood Purification. 20(4):370-375, 2002.
· Kristal-Boneh E et al. Association of calcitriol and blood pressure in normotensive men. Hypertension. 30(5):1289-1294, 1997.
· Li Y et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) is a negative endocrine regulator of the renin-angiotensin system. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 110(2):229-238, 2002.
· Li Y et al. Vitamin D regulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Journal of Cell Biochemistry. 88(2):327-331, 2003.
· Li Y et al. Vitamin D: a negative endocrine regulator of the renin-angiotensin system and blood pressure. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 89-90(1-5):387-392, 2004.
· Pfeifer M et al. Effects of a short-term vitamin D(3) and calcium supplementation on blood pressure and parathyroid hormone levels in elderly women. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 86(4):1633-1637, 2001.
· Sigmund C. Regulation of renin expression and blood pressure by vitamin D(3). Journal of Clinical Investigation. 110(2):155-156, 2002.
Vasquez A et al. The clinical importance of vitamin D (cholecalciferol): a paradigm shift with implications for all healthcare providers. Alternative Therapies. 10(5):28-38, 2004.
· Nimptsch K et al. Dietary intake of vitamin K and risk of prostate cancer in the Heidelberg cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 87:985-992, 2008.
· Habu D et al. Role of vitamin K2 in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in women with viral cirrhosis of the liver. JAMA. 292(3):358-361, 2004.
· Yoshida T et al. Apoptosis induction of vitamin K2 in lung carcinoma cell lines: the possibility of vitamin K2 therapy for lung cancer. International Journal of Oncology. 23(3):627-632, 2003.
· Lamson D and Plaza S. The anticancer effects of vitamin K. Alternative Medicine Review. 8(3):303-18, 2003.
Yokoyama T et al. Combination of vitamin K2 plus imatinib mesylate enhances induction of apoptosis in small cell lung cancer cell lines. International Journal of Oncology. 26(1):33-40, 2005.
· Chlebowski R et al. Vitamin K in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Treatment Review. 12:49-63, 1985.
· Lamson D et al. The anticancer effects of vitamin K. Alternative Medicine Review. 8(3):303-318, 2003.
· Hitomi M et al. Antitumor effects of vitamins K1, K2 and K3 on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. International Journal of Oncology. 26(3):713-720, 2005.
· Nouso K et al. Regression of hepatocellular carcinoma during vitamin K administration. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 11(42):6722-6724, 2005.
· Blackmore K et al. Vitamin D from dietary intake and sunlight exposure and the risk of hormone-receptor-defined breast cancer. American Journal of Epidemiology. 168(8):915-24, 2008.
· Deluca H et al. Vitamin D: its role and uses in immunology. FASEB Journal. 15(14):2579-2585, 2001.
Adorini L. Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D receptor ligands in autoimmune diseases. International Immunopharmacology. 2(7):1017-1028, 2002.
· Cantorna M et al. Mounting evidence for vitamin D as an environmental factor affecting autoimmune disease prevalence. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood). 229(11):1136-1142, 2004.
· Cantorna M. Vitamin D and autoimmunity: is vitamin D status an environmental factor affecting autoimmune disease prevalence? Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 223:230-233, 2000.
· Garland C et al. The role of vitamin D in cancer prevention. American Journal of Public Health. 96(2):252-61, 2006.
· Giovannucci E et al. Prospective study of predictors of vitamin D status and cancer incidence and mortality in men. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 98(7):451-459, 2006.
· Holick, M. Vitamin D: Its role in cancer prevention and treatment. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 92(1):49-59, 2006.
· Gorham E et al. Vitamin D and prevention of colorectal cancer. Journal Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 97(1-2):179-94, 2005.
· Grant W et al. Reviews: A critical review of studies on vitamin D in relation to colorectal cancer. Nutrition and Cancer. 48(2):115-123, 2004.
· Harris D et al. Vitamin D and colon carcinogenesis. Journal of Nutrition. 134(12):3463S-3471S, 2004.
· Hayes C et al. The immunological functions of the vitamin D endocrine system. Cellular and Molecular Biology. 49(2):277-300, 2003.
What makes Isotonix® Vitamin D with K2 product unique?
Isotonix Vitamin D with K2 contains vitamin D3, the metabolically active form of vitamin D, along with vitamin K2, a form of vitamin K which supports vascular health and calcium utilization. Vitamin D plays an important role in bone health, heart health and immune support while working with vitamin K to support normal absorption of calcium and promote healthy arteries. Isotonix Vitamin D is the first of its kind to deliver both of these powerful vitamins with isotonic delivery.
Vitamin K is included in Isotonix Vitamin D with K2 because of its unique partnership with vitamin D. Vitamins K and D work together to support calcium absorption and utilization. Vitamin K supports the normal delivery of calcium to the bones and promotes healthy arteries.
At least two naturally occurring forms of vitamin K have been identified and are known as K1 and K2. While there are many similarities between these two forms of vitamin K, they are distinguished by their important differences. The most significant difference between K1 and K2 is their chemical structure, which results in different pharmacokinetic properties. Vitamin K1 is retained primarily in the liver where, at high doses, it may interfere with the action of warfarin and other anticoagulant medications.
Vitamin K2 has a different mechanism of action. It is transported primarily to bones and blood vessels. Vitamin K2 helps to maintain bone mass, support calcium utilization and promote elasticity of blood vessels.
Some studies have concluded that vitamin K2 does not interfere with anticoagulant medications.* However, most products containing vitamin K (including K1 and/or K2) warn users taking anticoagulants not to take the product. If you are currently taking warfarin or another anticoagulant medication, you should consult your physician before taking any product containing vitamin K1 or K2.
Related terms: vitamin D, vitamin K, bone health, cardiovascular health, immune support, D3, K2
Frequently Asked Questions about Isotonix® Vitamin D with K2:
Why is vitamin K included in Isotonix® Vitamin D with K2?
Vitamin K is included in this product because of its unique partnership with vitamin D. Vitamins K and D work together to promote healthy calcium absorption and utilization. Vitamin K supports the delivery of calcium to the bones and helps maintain arterial health.*
Is Isotonix Vitamin D with K2 safe for people on anti-coagulant medications?
Some studies have concluded that vitamin K2 does not interfere with anticoagulant medications. However, most products containing vitamin K (including K1 and/or K2) warn users taking anticoagulants not to take the product. If you are currently taking warfarin or another anticoagulant medication, you should consult your physician before taking any product containing vitamin K1 or K2.
How do I take Isotonix Vitamin D with K2?
Mix one capful of Isotonix Vitamin D with K2 with 2 ounces of water. Take one serving daily.
Is it safe to take more than one serving of this product daily?
One serving daily of Isotonix Vitamin D with K2 is recommended. Check with your physician before taking additional daily servings of this product.
Is there a toxicity level for vitamin D?
The recommended daily Upper Limit for vitamin D is 10,000 IU, however, safety studies indicate that up to 40,000 IU may be safe for most people. If you wish to take more than one daily serving of this product, you should check with your physician.
What are dietary sources of vitamin D?
Foods rich in vitamin D include cod liver oil, salmon, mackerel and tuna.
For more information:
727-492-8212
www.orlampahealth.com
Orlampa Enterprises is a Trinity, Florida based company specializing in personalized health and wellness solutions. Primarily focused on growing its home Florida market since our inception, Orlampa Enterprises is primed to continue its growth by duplicating their proven business model of educating, training, and developing entrepreneurial leaders. Orlampa Enterprises seeks business owners and health professionals who are interested in developing mutually beneficial relationships based on their unique profit sharing system.
In addition to working with individuals and groups utilizing personalized wellness solutions, Orlampa Enterprises helps health care professionals implement science based wellness programs into their existing practice with the goal of educating the health care providers and their patients, while integrating a cash-based income stream into the health care providers’ facilities.
Orlampa Enterprises, Inc. is looking to network with health and wellness professionals and welcome the opportunity to discuss our expansion plans and how mutually beneficial relationships can be created. Please feel free to contact Phillip Black at pb@orlampa.com.

 Every year, billions are spent in fertility clinics; the result of which is often in vitro fertilization (IVF). About 5 years ago, I began receiving emails from a nurse practitioner in Indiana who works in a fertility clinic. Her experience was dramatic; 5,000 IU/day for both the man and woman frequently resulted in a healthy baby. However, her last email to me was quite sad, she was in danger of losing her job as her boss, a gynecologist, was losing money due to vitamin D. He ordered her to stop advocating it or lose her job.
Every year, billions are spent in fertility clinics; the result of which is often in vitro fertilization (IVF). About 5 years ago, I began receiving emails from a nurse practitioner in Indiana who works in a fertility clinic. Her experience was dramatic; 5,000 IU/day for both the man and woman frequently resulted in a healthy baby. However, her last email to me was quite sad, she was in danger of losing her job as her boss, a gynecologist, was losing money due to vitamin D. He ordered her to stop advocating it or lose her job.